Kopp–Neumann law
Kopp–Neumann law states that the specific heat C per unit mass (in J•kg−1•K−1) for alloys can be calculated from the following equation:
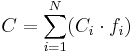
where: i - subsequent numbers from 1 to N, N - total number of alloy constituents, Ci and fi - specific heat and mass fraction of the i-th constituent.
References
- Frederick Seitz, The Modern Theory of Solids, McGraw-Hill, New York, USA, 1940, ASIN: B000OLCK08